The Era of Smart Lighting Is Coming
You can add lighting and building management to the list of industries caught in the disruptive undertow of the Internet of Things.
The combination of light-emitting diode (LED) technology and Power over Ethernet (PoE), coupled with IoT connectivity, is creating a wave of change now hitting both of these industries.
Look no further than Cisco Systems, which is partnering with intelligent lighting systems developer Philips and LED innovator Cree on smart lighting. Cisco is launching its Digital Ceiling solution and is targeting organizations that want to harness energy savings and expand centralized control over their office workspaces.
Bringing IoT insights into everyday work environments promises to deliver valuable efficiencies and innovative productivity gains to how work gets done.
Moving to a Smart Ceiling
Why the ceiling? It took a couple of important innovations to get us to the smart lighting era.
First is LED technology, which converts electricity directly into light — a huge leap up from the traditional incandescent light bulb, which needs to generate heat in order to create light.
Second is improvements in PoE technology, although there are several competing connectivity and power platforms in development besides PoE. Traditionally used to carry power and data to and from devices on a local area network, it’s now being used in smart lighting in the same capacity, transporting power and data for LED fixtures connected to the LAN.
Once they sprinkle some IoT secret sauce on top of all of this, businesses have endless possibilities for gathering data to then guide manipulation of the work environment. And thanks to Ethernet connectivity, businesses now have this infrastructure on the IP network, allowing for centralized management.
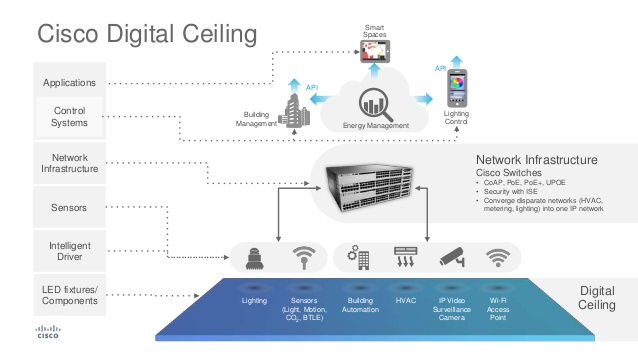
For building facilities teams, this is a major development. Disparate building systems — including lighting, HVAC, metering, blinds, CCTV, security and analytics — can now be centrally powered and controlled on a single network.
Lighting Up IoT Sensors
The most common sensors being rolled out now are temperature, humidity and presence — in part because cooling, lighting and ventilation account for 62 percent of electricity use in commercial buildings, says Rob Boyd, host of Cisco’s TechWiseTV.
Being able to tackle these costs via IoT capabilities was a logical choice; hence, the focus on adding these sensors to the LED fixture. In fact, one early adopter, the Central Iowa Power Cooperative, saw a 75 percent decrease in lighting-related energy costs following installation.
Just installing LEDs instead of incandescent bulbs has an impact not just on lighting costs, but thermal and HVAC as well. And with the introduction of sensors, rooms can then be programmed to dynamically adjust temperature and lighting, depending on whether or not a person is present.
Gaining Additional Efficiencies
With Ethernet, these LED fixtures are plug and play, which means it is much easier and more efficient to swap out lighting fixtures and there is no need to shut off all the power on a line to rip and replace a single fixture.
Smart lighting allows building facilities teams to be more proactive, reconfiguring the workspace dynamically as needed, more safely and quickly.
Cable runs are another win-win area. With a Gigabit Ethernet port every 8 feet (mounted to the back of the light fixture to provide connectivity), businesses can avoid lengthy cable runs to a dist ant wire closet, reducing cabling and power costs.
Like many areas of IoT, smart lighting is still a nascent development. The first wave of activity, which we’re just now seeing, is installing connected LED lighting on the network. It may take several years for smart lighting to become widely adopted.
The second wave will be using IoT to bring automation to all those endpoints on the IP network. But the potential is huge, with a predicted global market of $47 billion by 2020.









