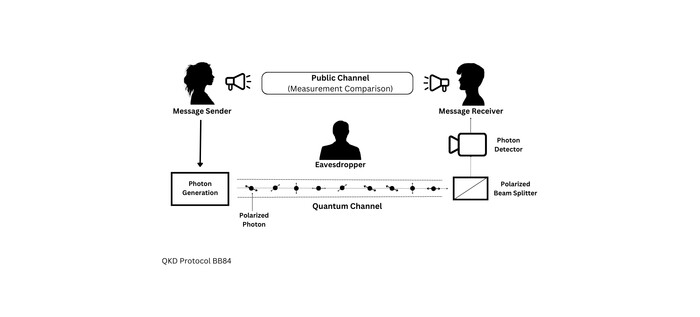
What Are Some QKD Challenges in Business?
Here are four of the most pressing challenges businesses might encounter with QKD that IT leaders need to know:
QKD is expensive. Hardware cost is one of the largest hurdles businesses faces when implementing QKD. For example, a fiber-optic network system, which acts as a quantum channel to transmit photons from sender to receiver, is expensive. Unless a business already owns a network system that connects it with its customers, it will have to either install one — which could cost between $5,000 and $60,000 per mile — or lease “dark fiber” from a supplier and pay a substantial upfront cost with recurring maintenance fees.
There are also costs for other hardware components, such as photon detectors, lasers, semiconductor chips, specialized cooling equipment and more. However, the more commercially available QKD hardware becomes, the less it will cost.
QKD photons can only travel so far. One of QKD’s most troubling limitations is that photons struggle to travel long distances. As they weaken, transmission often fails. This limitation makes it harder for businesses with customers across multiple states or countries to use QKD.
To solve this, businesses would need to contract with trusted third-party relay stations. A relay station is an intermediary node that can send photons over longer distances. Though doable, this too can be costly. Soon, however, IT leaders may be able to use quantum repeaters, which act as an intermediary between the sender and receiver, copying optical signals from the sender and retransmitting them to the receiver over a longer distance. Placing quantum repeaters between nodes would allow photons to be carried farther. But right now, quantum repeaters are still in the developmental stage.
Click the banner below to read the 2024 CDW Cybersecurity Research Report.