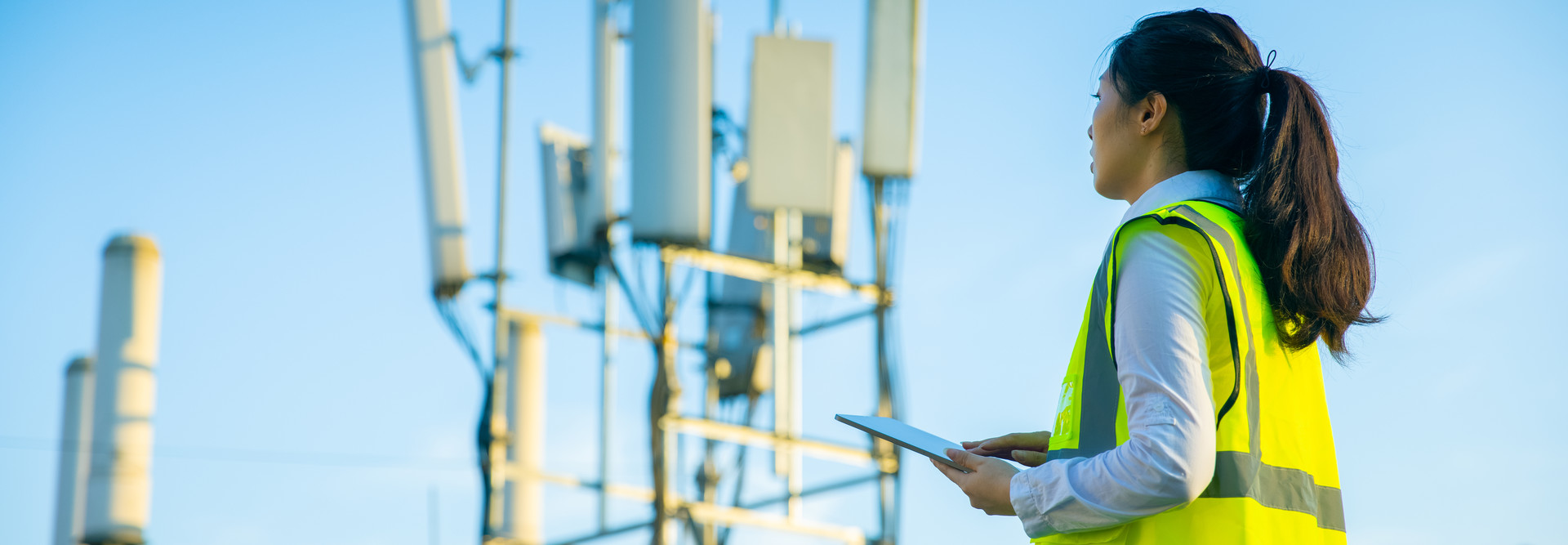
Bolstering smart grid technology with 5G enables increased automation across smart grids.
Exploring this for the European Union’s Service Oriented Grid for the Network of the Future (SOGNO) project, a consortium of 13 companies led by Ericsson developed a scalable, cost-efficient automation solution.The team confirmed that, combined with edge computing, 5G can be harnessed to virtualize automation services within the 5G edge infrastructure.
“SOGNO has proven that 5G can support near real-time power distribution automation services,” says Fiona Williams, a research director at Ericsson, in the corresponding case study.
Even without 5G, smart grids operate more efficiently than traditional grids. With 5G, this efficiency is maximized even further. By supporting increased connectivity and automation, 5G can improve smart grid technologies, enabling more efficient energy management and enhanced distribution — saving time, labor and financial resources, which means more green, sustainable efforts for companies.
READ MORE: How 5G WAN provides flexibility and reliability.
Getting Started with 5G Technology
Adoption of 5G is expected to increase rapidly over the next few years, from 236 million global subscriptions currently to more than 3 billion by 2025.
IT leaders who haven’t made the switch should first consider the opportunities 5G offers and how it can be optimized for their organization. Start with the basics: Identify core networking objectives, budget and timeline (from consultation to implementation). Next, do some thoughtful research. Many providers, including Cradlepoint and Verizon, offer 5G but also conduct assessments to gauge the strength of an organization’s current network and its capacity for growth.
DISCOVER: How CDW can support your energy and utilities modernization efforts.
5G Use Cases in the E&U Industry
5G has an abundance of E&U use cases, including smart grids, augmented reality and predictive maintenance. These can be broadly categorized into three primary types of connected services:
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband: 5G eMBB focuses on high-speed transmission of end-user data and system capacity. In other words, whether it’s to rapidly transfer files to a secure location or maintain a clear, real-time connection for a virtual conference call, 5G technology provides a faster, more reliable experience for users. It also connects a variety of applications that may not have been technologically feasible before the advent of 5G.
- Mission-Critical Communications: 5G technology provides the ultrareliable low-latency communication essential for mission-critical applications, ensuring that messages are delivered quickly and completely, even in situations with network congestion or interference. Additionally, 5G supports private networks and supports network slicing — a network configuration that allows for multiple virtual and independent networks to be created on top of a common physical infrastructure.
- Massive Internet of Things: The 5G standard for massive IoT can support up to 1 million connected devices for roughly every 1 square kilometer. That’s partly why 5G-based IoT connections are expected to reach 116 million globally by 2026.
With the enhanced speed, capacity and coverage documented by these use cases, 5G is poised to become the go-to first choice for many E&U companies and users.